
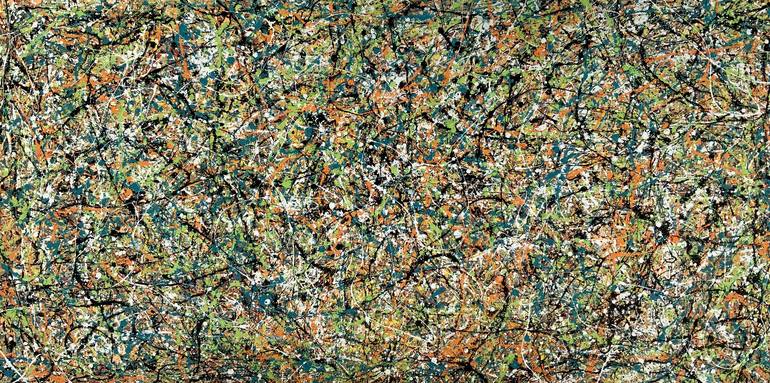






VIEW IN MY ROOM
Bonk's Adventure Painting
Painting, Acrylic on Canvas
Size: 80 W x 40 H x 1.5 D in
Ships in a Crate
Shipping included
14-day satisfaction guarantee
Artist Recognition

Artist featured in a collection
About The Artwork
Bonk's Adventure is a scrolling platform game developed by Red Company and Atlus and released in 1989 in Japan and 1990 in North America for the TurboGrafx-16. In Japan it was titled PC Genjin (PC原人), a play on the Japanese name for the system, PC Engine. The first game in the Bonk series, it was followed by two more games for the TurboGrafx-16 before branching out to other platforms. Bonk's Adventure was ported to the NES and Amiga, as well as being released as a coin-operated arcade game, under different titles (FC Genjin and BC Genjin). A completely different game with the same name appeared on the Game Boy (under the title GB Genjin in Japan). The game's protagonist is Bonk, a strong and bald caveboy who battles anthropomorphic dinosaurs and other prehistoric enemies. Bonk's mission is to rescue Princess Za (a small pink Pleisiosaur-type reptile) who has been kidnapped by the evil King Drool (a large, green, Tyrannosaurus-type dinosaur). In the arcade version, Bonk is also assisted by a female version of himself. The Japanese name for the original game for the PC-Engine is PC-Genjin (PC原人, in English: PC-Caveman). In Japanese, PC-Genjin sounds like PC-Engine, and the PC stands for Pithecanthropus Computerus, a pun on Pithecanthropus erectus. It is generally called PC-Kid in English, as he was meant to be NEC's mascot at the time. Later, when the game was ported (or given different versions) for other platforms, it was renamed accordingly, like FC-Kid (after Family Computer, the original Japanese name for the NES, and the FC stood for Freakthoropus Computerus), GB-Kid (after the Game Boy), or the more generic name BC-Kid in some other versions, including Amiga. In North America, this was scrapped, as the game name is always Bonk's Adventure or something similar. Red Entertainment (株式会社レッド・エンタテインメント, Kabushiki-gaisha Reddo Entateinmento) is a video game developer and publisher based in Japan. Formerly known as the Red Company (レッドカンパニー, Reddo Kanpanī) since its founding in 1976 (though it did not begin doing business until 1985), it was reorganized under its current moniker on December 4, 2000. While Red Company as a public corporation dates back to the mid-1980s, the first title released under the Red Entertainment brand was Gungrave on July 17, 2002. The name "RED" comes from "Royal Emperor Dragon". In 2011, the company was acquired by Chinese game developer UltiZen Games Limited. In 2014, Red Entertainment was sold to Oizumi Corporation. Atlus Co., Ltd. (株式会社アトラス, Kabushiki gaisha Atorasu) is a Japanese video game developer, publisher, and distribution company based in Tokyo. A subsidiary of Sega, the company is known for its Megami Tensei, Persona, Etrian Odyssey, and Trauma Center series, among others. Its corporate mascot is Jack Frost, a snowman-like character from their Shin Megami Tensei series. Outside of games, the company is also known for their purikura services, which are selfie photo sticker booths popular in East Asia. Atlus was established in April 1986 and spent its early years as a video game developer for other companies. It became a video game publisher of its own in 1989 and existed until it was merged into Index Corporation in October 2010. After the dissolution, the name Atlus continued as a brand used by Index Corporation for video game publishing until 2013, when it was bought by Sega and revived as a company initially under the name Sega Dream Corporation. Atlus has three development divisions: Creative Department 1st Production (Team Maniax), Creative Department 2nd Production (P-Studio), and Creative Department 3rd Production (Studio Zero). A North American branch of the company, Atlus USA was founded in 1991 in order to focus on publishing and localizing games for North America, while a European branch was founded in 2017. The TurboGrafx-16, known as the PC Engine in Japan and France, is a fourth-generation home video game console designed by Hudson Soft and sold by NEC Home Electronics. It was the first console marketed in the 16-bit era, although in reality it used a modified 8-bit CPU. It was released in Japan in 1987 and in North America in 1989. The Japanese model was imported and distributed in France in 1989, and the United Kingdom and Spain received a version based on the American model known as simply TurboGrafx. In Japan, the system was launched as a competitor to the Famicom, but the delayed United States release meant that it ended up competing with the Sega Genesis and later the Super Nintendo Entertainment System. The TurboGrafx-16 has an 8-bit CPU, a 16-bit video color encoder, and a 16-bit video display controller. The GPUs are capable of displaying 482 colors simultaneously, out of 512. With dimensions of just 14 cm × 14 cm × 3.8 cm (5.5 in × 5.5 in × 1.5 in), the Japanese PC Engine is the smallest major home game console ever made. Games were released on HuCard cartridges and later the CD-ROM optical format with the TurboGrafx-CD add-on. The TurboGrafx-16 failed to break into the North American market and sold poorly, which has been blamed on the delayed release and inferior marketing. Despite the "16" in its name and the marketing of the console as a 16-bit platform, it used an 8-bit CPU, a marketing tactic that was criticized by some as deceptive. However, in Japan, the PC Engine, introduced into the market at a much earlier date, was very successful. It gained strong third-party support and outsold the Famicom at its 1987 debut, eventually becoming the Super Famicom's main rival. At least 17 distinct models of the TurboGrafx-16 were made, including portable versions and those that integrated the CD-ROM add-on. An enhanced model, the PC Engine SuperGrafx, was rushed to market in 1989. It featured many performance enhancements and was intended to supersede the standard PC Engine. It failed to catch on - only six titles were released that took advantage of the added power and it was quickly discontinued. The entire series was discontinued in 1994. It was succeeded by the PC-FX, which was released only in Japan. Source: Wikipedia
Details & Dimensions
Painting:Acrylic on Canvas
Original:One-of-a-kind Artwork
Size:80 W x 40 H x 1.5 D in
Frame:Not Framed
Ready to Hang:Not applicable
Packaging:Ships in a Crate
Shipping & Returns
Delivery Time:Typically 5-7 business days for domestic shipments, 10-14 business days for international shipments.
Handling:Ships in a wooden crate for additional protection of heavy or oversized artworks. Crated works are subject to an $80 care and handling fee. Artists are responsible for packaging and adhering to Saatchi Art’s packaging guidelines.
Ships From:United States.
Have additional questions?
Please visit our help section or contact us.
I’m (I am?) a self-taught artist, originally from the north suburbs of Chicago (also known as John Hughes' America). Born in 1984, I started painting in 2017 and began to take it somewhat seriously in 2019. I currently reside in rural Montana and live a secluded life with my three dogs - Pebbles (a.k.a. Jaws, Brandy, Fang), Bam Bam (a.k.a. Scrat, Dinki-Di, Trash Panda, Dug), and Mystique (a.k.a. Lady), and five cats - Burglekutt (a.k.a. Ghostmouse Makah), Vohnkar! (a.k.a. Storm Shadow, Grogu), Falkor (a.k.a. Moro, The Mummy's Kryptonite, Wendigo, BFC), Nibbler (a.k.a. Cobblepot), and Meegosh (a.k.a. Lenny). Part of the preface to the 'Complete Works of Emily Dickinson helps sum me up as a person and an artist: "The verses of Emily Dickinson belong emphatically to what Emerson long since called ‘the Poetry of the Portfolio,’ something produced absolutely without the thought of publication, and solely by way of expression of the writer's own mind. Such verse must inevitably forfeit whatever advantage lies in the discipline of public criticism and the enforced conformity to accepted ways. On the other hand, it may often gain something through the habit of freedom and unconventional utterance of daring thoughts. In the case of the present author, there was no choice in the matter; she must write thus, or not at all. A recluse by temperament and habit, literally spending years without settling her foot beyond the doorstep, and many more years during which her walks were strictly limited to her father's grounds, she habitually concealed her mind, like her person, from all but a few friends; and it was with great difficulty that she was persuaded to print during her lifetime, three or four poems. Yet she wrote verses in great abundance; and though brought curiosity indifferent to all conventional rules, had yet a rigorous literary standard of her own, and often altered a word many times to suit an ear which had its own tenacious fastidiousness." -Thomas Wentworth Higginson "Not bad... you say this is your first lesson?" "Yes, but my father was an *art collector*, so…"
Artist Recognition

Artist featured by Saatchi Art in a collection
Thousands Of Five-Star Reviews
We deliver world-class customer service to all of our art buyers.
Global Selection
Explore an unparalleled artwork selection by artists from around the world.
Satisfaction Guaranteed
Our 14-day satisfaction guarantee allows you to buy with confidence.
Support An Artist With Every Purchase
We pay our artists more on every sale than other galleries.
Need More Help?